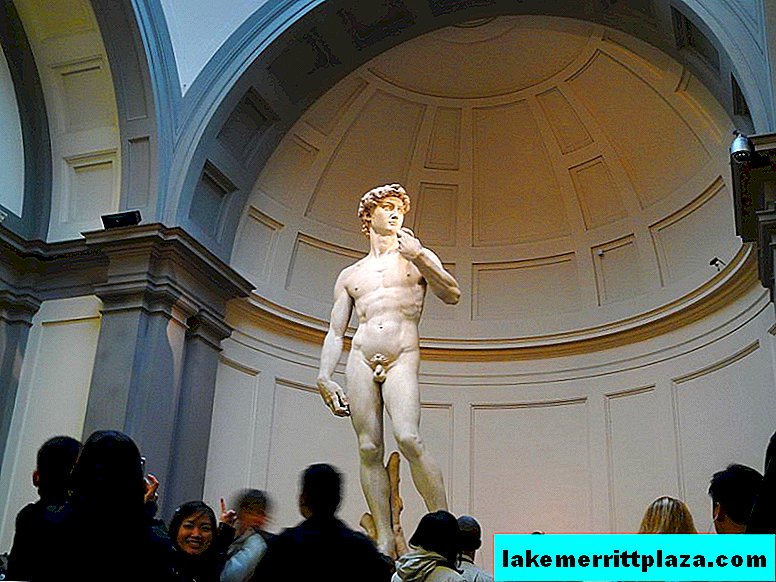
The statue of David by the great Michelangelo is one of the most impressive works of the Italian Renaissance. This sculpture is considered the perfect ideal of masculine beauty. Today, David can be seen at the Academy of Fine Arts.
"David" by Michelangelo Buonarotti - an invaluable masterpiece of the Italian Renaissance, photo isra
The statue of David by the great Michelangelo (David di Michelangelo Firenze) is one of the most impressive works of the Italian Renaissance. This sculpture is considered the perfect ideal of masculine beauty.
Today, "David" can be seen in the building of the Florentine Academy of Fine Arts. On Signoria Square, where the statue originally stood, a copy is now installed.
David Creation Version
There is a version of the creation of the masterpiece described in the work of Giorgio Vasari. According to this story, a huge block of marble, intended for sculpture, was corrupted by an inept sculptor. Leonardo da Vinci suggested correcting the work, but the celebrated master refused indignantly. Then the material was given to the young talented Michelangelo, and the sculptor amazed everyone with his creation.
About sculpture

David at the Academy of Fine Arts, photo b.fabio85
"David" was installed on the Piazza Signoria near the Palazzo Vecchio in September 1504. The height of the marble statue was 516 cm. Its scale testifies to the skill of Michelangelo. He did not make a full-sized clay model, but fashioned only a small wax prototype. While working on fragments of the sculpture, he saw only a small part of it nearby - however, all the proportions of David's figure and facial features were perfectly observed.
Marble David looks formidable and confident, full of inner strength. The hero is preparing for a fight with Goliath: in the hand of his sling, the muscles are tense. In anticipation of the enemy, the gaze of a young shepherd is directed towards the Arno River. David is depicted naked, in the spirit of ancient statues, but his nakedness only emphasizes calm and freedom.
Placement and damage to the statue
The authorities of Florence were delighted with the work of Buonarotti. The statue was placed in a special wooden tower (a marble statue was hung in a box to protect it from impacts during transportation). Troubles awaited the creation of Michelangelo at the time of transportation: a group of young people, supporters of the Medici dynasty, attacked the procession. They sought to capture and destroy the symbol of the republican government. Fortunately, the plan of the rebels failed.

Marble Statue of David by Michelangelo, photo by Pete Riches
In 1512, lightning struck the pedestal, but the elements did not damage the marble figure. In April 1527, during the second expulsion of the Medici from the city, supporters of the republic took refuge in the Palazzo Vecchio. They threw stones and furniture from the windows, and caused several damage to the statue. Chipped fragments were collected and hidden by Francesco Salviati and Giorgio Vasari. Later, the defects were eliminated, but their traces are still visible.
For centuries, the surface of marble has been destroyed by wind and moisture. The statue needed restoration - it was carried out in 1843 by Lorenzo Bartolini. The methods of that time were crude: marble was cleaned with cutting tools and hydrochloric acid, irreparable damage was caused to the upper layer of the material.
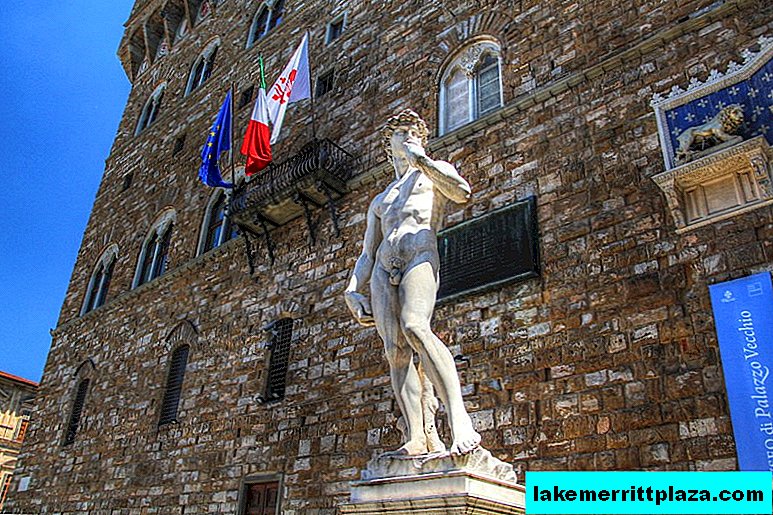

Copy of David's sculpture at Signoria Square, photo by Alan-Studt
To stop the destruction of the masterpiece, it was decided to move “David” to the Academy of Fine Arts. At the end of the Academy's Art Gallery, architect Emilio de Fabrice built a new pedestal. The statue was transported with unprecedented safety precautions in a complex wooden cart. In August 1873 she took a new place, but for several years she stood packed in a box. Only in July 1882, the creation of Michelangelo was open to the public.
In 1991, already at the Academy, there was a new attempt on David. The mad Pierrot Canata attacked the statue with a hammer. He managed to damage two fingers of his left foot on the sculpture. The damage has been eliminated, but traces of it are still visible.
Restoration
The capital restoration of the Buonarotti masterpiece was carried out in 2003, in the Florentine workshop for the processing of semiprecious stones Opificio delle pietre dure. By the 500th anniversary of the creation of a priceless statue, experienced craftsmen have completely cleaned it of the pollution accumulated over the centuries.
Sculpture of David (Michelangelo)
Via Bettino Ricasoli, 60 50122 Firenze Italy
uffizi.firenze.itTake bus 1, 6, 11, 14, 17, 19, 23, 31, 52, 54, 82, C1, G to the Piazza Di San Marco stop








